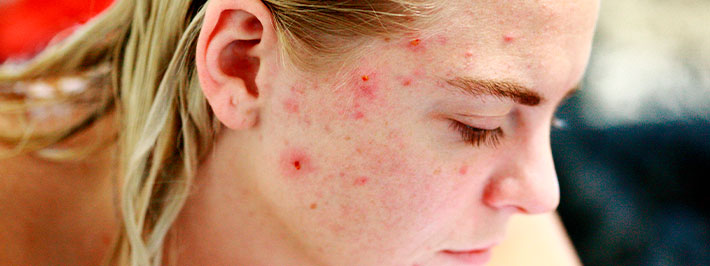
Acne in summer: can the sun cause pimples?
Advice for acne-prone skin: Certain medications make the skin hypersensitive to the sun. And the sun is a false friend for you! How to live summer to the fullest when you have acne pimples? What treatments are prohibited? What precautions to take in summer when you are exposed to the sun and have acne? Expert advice.
In the summer, anyone with acne should think twice about partying in the sun. Whether it affects your face, décolletage, or upper back, acne doesn't like the sun. Another problem: Many acne medications are photosensitizing: they can trigger skin rashes on areas exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays—face, hands, forearms, shoulders. If you dare to wear a swimsuit, the rash can spread all over your body.
Is the sun good for acne?
No, the sun is a false friend for acne-prone skin. After summer and sun exposure, teenagers, but not only them, are sometimes affected by acne breakouts a few weeks after returning from vacation.
"Tanning may suggest that exposure can cure acne, quite the opposite. The sun is a bad friend for people with acne," says the National Union of Dermatologists and Venerologists.
The risk is twofold to develop:
Possible aggravation during exposures;
A push of pimples related to this exposure that can occur a few weeks after returning from vacation.
Small pimples, blackheads, pigmentation problems, skin dryness, seborrhea. Many skin problems can be the result of overexposure to the sun's rays.
Rebound effect: why is sun exposure bad for acne?
So why is the sun such a bad friend for acne-prone skin? Because at the beginning of the exposure, under the effect of UV rays, the superficial layer of the skin thickens and the lesions subside. Which can prompt people to expose themselves more. But beware of the rebound effect: the lesions that had disappeared return a few days or weeks after exposure, with regrowth that may be more important.
"It is therefore very important to protect yourself during the holidays during sun exposure and to explain this to adolescents who often tend, at this age, to expose themselves too much", recommends the Union.
In case of overexposure to the sun or poorly applied sunscreen, there is a risk of seborrhea: as the skin dries, the sebum-producing sebaceous glands produce excessive amounts of sebum, causing pimples and comedones to appear.
Acne pimple scars on the face.
Excessive exposure to the sun can also cause pigmentation problems: people who suffer from acne or who have acne scars are particularly prone to hyperpigmentation, which is characterized in particular by the appearance of dark spots on the skin.
How to avoid acne breakouts during and after the summer?
Protect yourself from the sun with the right protection. Apply sunscreen 15 to 30 minutes before exposure, then every two hours. Its protection factor will be equal to 50 and the anti-UVA coefficient less than or equal to 2. It must not be comedogenic (susceptible to favoring the formation of blackheads). Choose a fluid, non-greasy sunscreen, therefore preferably water-based and oil-free or fragrance-free to avoid any irritation or photosensitization. Prefer sun creams based on mineral filters (titanium dioxide, zinc oxide) that reflect light and UV rays instead of absorbing them.
Wear a t-shirt and a hat, which are the best photoprotectors. People who suffer from severe acne are at greater risk of depigmentation from the sun, especially at the level of scarring. Sun protection, again, is essential. Avoid UV rays and sun exposure between 12 and 16 hours.
Remember to rinse your face after sweating or swimming in the sea or pool to remove all residue of sweat, sand, salt and chlorine from your skin. Moisturize your skin several times a day, with a moisturizing cream that is more or less greasy depending on the treatment and is non-comedogenic.